Shopping Cart
0 item(s) - $0.00Estradiol ELISA
Availability: In Stock
Add to Compare
Enzyme Immunoassay for the Quantitative Determination of Estradiol (E2) Concentration in Human Serum
FOR RESEARCH USE ONLY. NOT FOR USE IN DIAGNOSTIC PROCEDURES
SUMMARY
Estradiol is a human sex hormone and steroid, and the primary female sex hormone. It is named for and is important in the regulation of the estrous and menstrual female reproductive cycles. Estradiol is essential for the development and maintenance of female reproductive tissues but it also has important effects in many other tissues including bone. While estrogen levels in men are lower compared to women, estrogens have essential functions in men as well. Estradiol is found in most vertebrates as well as many crustaceans, insects, fish, and other animal species. Estradiol is produced especially within the follicles of female ovaries, but also in other endocrine (i.e., hormone-producing) and non-endocrine tissues (e.g., including fat, liver, adrenal, breast, and neural tissues). Estradiol is biosynthesized from progesterone (arrived at in two steps from cholesterol, via intermediate pregnenolone). One principle pathway then converts progesterone to its 17-hydroxy-derivative, and then to androstenedione via sequential cytochrome P450-catalyzed oxidations. Action of aromatase on this dione generates estrone, and action of a dehydrogenase on this gives the title compound, 17-estradiol.
PRINCIPLE OF THE TEST
The United Immunoassay E2 EIA is based on the principle of competitive binding between E2 in the test specimen and E2-HRP conjugate for a constant amount of rabbit anti-Estradiol. In the incubation, goat anti-rabbit IgG-coated wells are incubated with 25 ?l E2 standards, controls, patient samples, 100 ?l Estradiol-HRP Conjugate Reagent and 50 ?l rabbit anti-Estradiol reagent at room temperature (18-25°C) for 90 minutes. During the incubation, a fixed amount of HRP-labeled E2 competes with the endogenous E2 in the standard, sample, or quality control serum for a fixed number of binding sites of the specific E2 antibody. Thus, the amount of E2 peroxidase conjugate immunologically bound to the well progressively decreases as the concentration of E2 in the specimen increases. Unbound E2 peroxidase conjugate is then removed and the wells washed. Next, a solution of TMB Reagent is added and incubated at room temperature for 20 minutes, resulting in the development of blue color. The color development is stopped with the addition of 1N HCl, and the absorbance is measured spectrophotometrically at 450 nm. The intensity of the color formed is proportional to the amount of enzyme present and is inversely related to the amount of unlabeled E2 in the sample. A standard curve is obtained by plotting the concentration of the standard versus the absorbance. The E2 concentration of the specimens and controls run concurrently with the standards can be calculated from the standard curve.
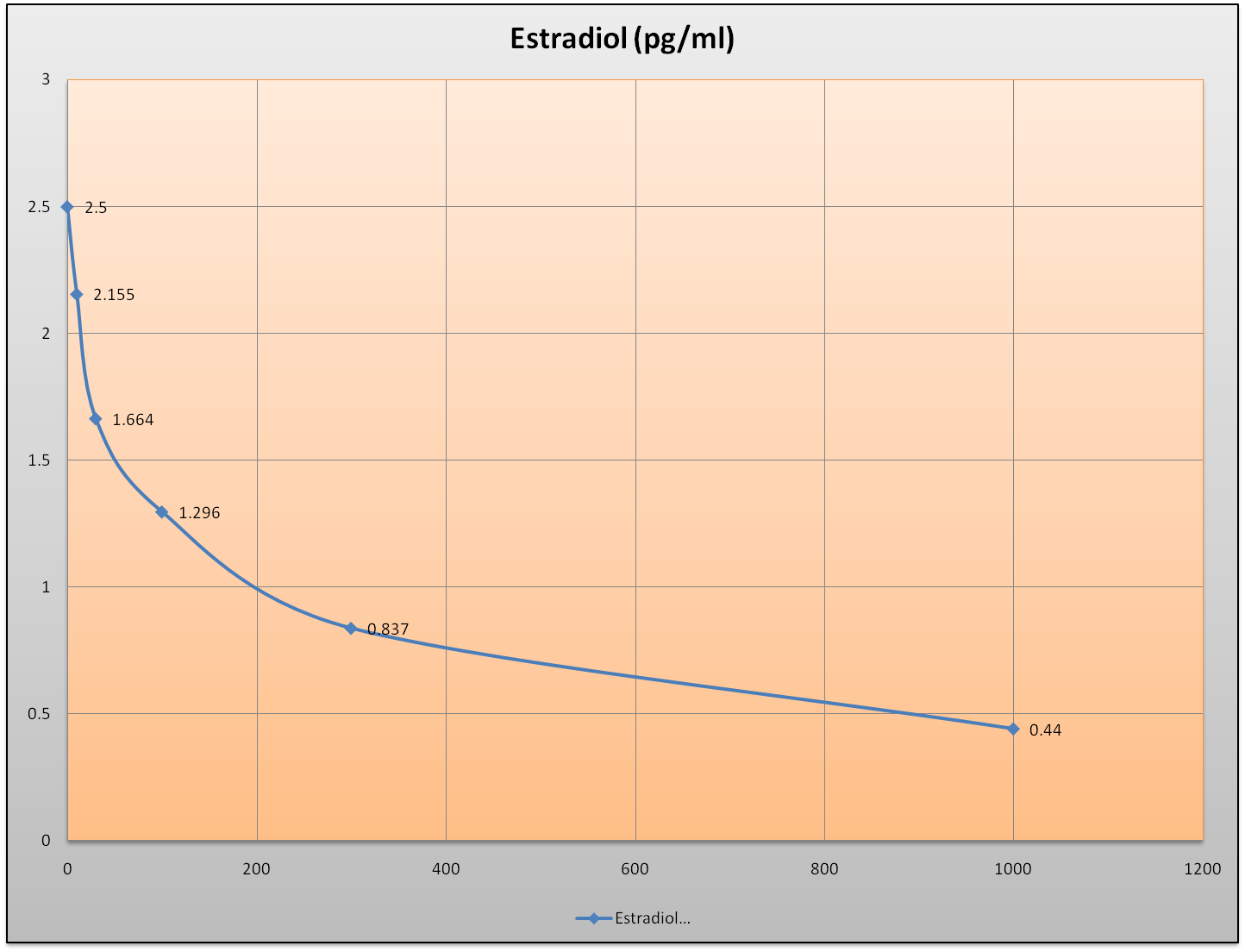
EXAMPLE OF STANDARD CURVE
Results of a typical standard run with optical density readings at 450 nm shown in the Y axis against Estradiol concentrations shown in the X axis. This standard curve is for the purpose of illustration only, and should not be used to calculate unknowns. Each user should obtain his or her own data and standard curve.
| General | |
| ANALYTE GROUP | Estradiol |
| GROUPING | Hormones:Reproduction |
| PRODUCT NAME | ELISA |
| STORAGE | Store the kit at 2-8°C |
| COUNTRY OF ORIGIN | USA |
| DISCOUNTS | Bulk Packaging; High Volume |
| ELISA | |
| TESTS PER KIT | 96 (12 x 8) |
| CALIBRATION RANGE | 0 - 1,000 pg/mL (Recommended) |
United Immunoassay, Inc. © 2026